Hyperlink vs URL
Summary: Difference Between Hyperlink and URL is that most Web pages contain links. A link, short for hyperlink, is a built-in connection to another related Web page or part of a Web page. While every Web page has a unique address, which is called a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) or Web address.
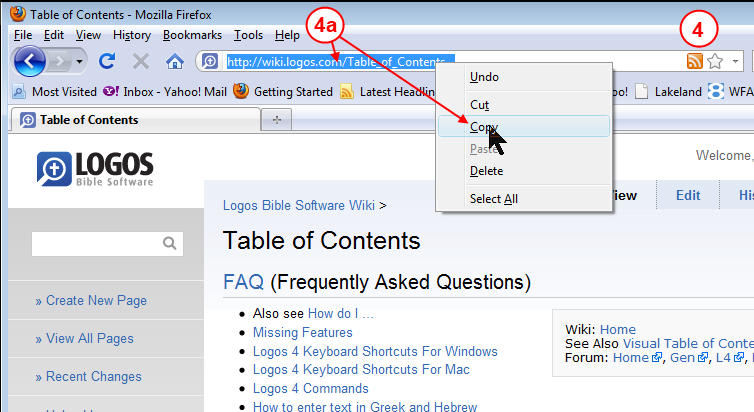
Hyperlink
Most Web pages contain links. A link, short for hyperlink, is a built-in connection to another related Web page or part of a Web page. Links allow you to obtain information in a nonlinear way. That is, instead of accessing topics in a specified order, you move directly to a topic of interest. Branching from one related topic to another in a nonlinear fashion is what makes links so powerful. Some people use the phrase, surfing the Web, to refer to the activity of using links to explore the Web. A link can be text or an image. Text links may be underlined and/or displayed in a color different from other text on the Web page. Pointing to, or positioning the pointer on, a link on the screen typically changes the shape of the pointer to a small hand with a pointing index finger. Pointing to a link also sometimes causes the link to change in appearance or play a sound. The Web page contains a variety of link types, with the pointer on one of the links.
URL
A Web page has a unique address, which is called a URL (Uniform Resource Locator) or Web address. For example, the home page for the United States National Park Service Web site has a Web address of http://www.nps.gov. A Web browser retrieves a Web page using its Web address.
If you know the Web address of a Web page, you can type it in the Address bar at the top of the browser window. If you type http://www.nps.gov/grsm/planyourvisit/wildlifeviewing.htm as the Web address in the Address bar and then press the enter key, the browser downloads and displays the Web page shown in Figure 2-6.
A Web address consists of a protocol, domain name, and sometimes the path to a specific Web page or location on a Web page. Many Web page addresses begin with http://. The http, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol, is a set of rules that defines how pages transfer on the Internet. To help minimize errors, many browsers and Web sites do not require you enter the http:// and www portions of the Web address.
When you enter the Web address, http://www.nps.gov/grsm/planyourvisit/wildlifeviewing.htm in the Web browser, it sends a request to the Web server that contains the nps.com Web site. The server then retrieves the Web page that is named wildlifeviewing.htm in the grsm/planyourvisit path and delivers it to your browser, which then displays the Web page on the screen.
To save time, many users create bookmarks for their frequently visited Web pages. A bookmark, or favorite, is a saved Web address that you access by clicking the bookmark name in a list. That is, instead of entering a Web address to display a Web page, you can click a previously saved bookmark.
Also Read:
Difference Between Search Engine and Directory
Difference Between Browser and Search Engine
Difference Between Web Address and Email Address
Difference Between Domain and Hosting
Difference Between www and Internet
Difference Between www and www2





Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.