Microtubules vs Microfilaments
Summary: Difference Between Microtubules and Microfilaments is that Microtubules are the straight, hollow and tubular structures of the cytoskeleton. While Microfilaments are long and fine threadlike structures with a diameter of about 3 to 6 nm. These filaments are made up of non-tubular contractile proteins called actin and myosin.
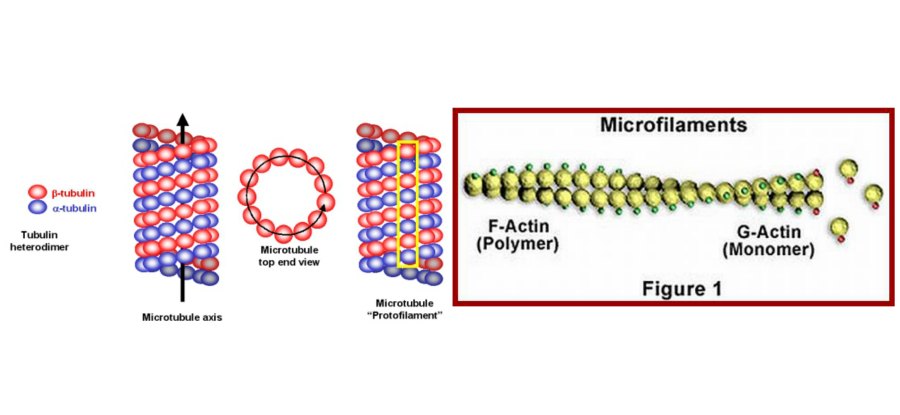
Microtubules
Microtubules are the straight, hollow and tubular structures of the cytoskeleton. These organelles without the limiting membrane are arranged in different bundles. Each tubule has a diameter of 20 to 30 nm. Length of microtubule varies and it may be 1000 times more than the thickness. Structurally, the microtubules are formed by bundles of globular protein called tubulin. Tubulin has two subunits, namely αsubunit and βsubunit.
Functions of microtubules
- Microtubules may function alone or join with other proteins to form more complex structures like cilia, flagella or centrioles and perform various functions. Microtubules:
- Determine the shape of the cell
- Give structural strength to the cell
- Act like conveyer belts which allow the movement of granules, vesicles, protein molecules and some organelles like mitochondria to different parts of the cell
- Form the spindle fibers which separate the chromosomes during mitosis
- Are responsible for the movement of centrioles and the complex cellular structures like cilia.
Microfilaments
Microfilaments are long and fine threadlike structures with a diameter of about 3 to 6 nm. These filaments are made up of non-tubular contractile proteins called actin and myosin. Actin is more abundant than myosin. Microfilaments are present throughout the cytoplasm. The microfilaments present in ectoplasm contain only actin molecules and those present in endoplasm contain both actin and myosin molecules.
Functions of microfilaments
Microfilaments:
- Give structural strength to the cell
- Provide resistance to the cell against the pulling forces
- Are responsible for cellular movements like contraction, gliding and cytokinesis (partition of cytoplasm during cell division)
Also Read:
Difference Between Microtubules and Intermediate Filaments
Difference Between Intermediate Filaments and Microfilaments
Difference Between Sexual and Asexual Reproduction


Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.