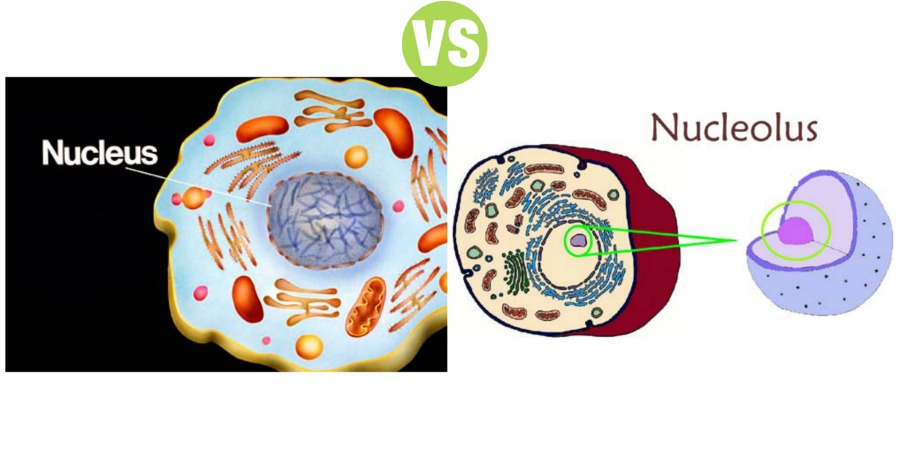
Nucleus and Nucleolus
Summary: Difference Between Nucleus and Nucleolus is that Nucleolus is a small, round granular structure of the nucleus. Each nucleus contains one or more nucleoli. While Nucleus is the most prominent and the largest cellular organelle. It has a diameter of 10 µ to 22 µ and occupies about 10% of total volume of the cell.
Nucleolus
Nucleolus is a small, round granular structure of the nucleus. Each nucleus contains one or more nucleoli. The nucleolus contains RNA and some proteins, which are similar to those found in ribosomes. The RNA is synthesized by five different pairs of chromosomes and stored in the nucleolus. Later, it is condensed to form the subunits of ribosomes. All the subunits formed in the nucleolus are transported to cytoplasm through the pores of nuclear membrane. In the cytoplasm, these subunits fuse to form ribosomes, which play an essential role in the formation of proteins.
Nucleus
Nucleus is the most prominent and the largest cellular organelle. It has a diameter of 10 µ to 22 µ and occupies about 10% of total volume of the cell. Nucleus is present in all the cells in the body except the red blood cells. The cells with nucleus are called eukaryotes and those without nucleus are known as prokaryotes. Presence of nucleus is necessary for cell division.
Most of the cells have only one nucleus (uninucleated cells). Few types of cells like skeletal muscle cells have many nuclei (multinucleated cells). Generally, the nucleus is located in the center of the cell. It is mostly spherical in shape. However, the shape and situation of nucleus vary in some cells.
STRUCTURE OF NUCLEUS
Nucleus is covered by a membrane called nuclear mem – brane and contains many components. Major components of nucleus are nucleoplasm, chromatin and nucleolus.
FUNCTIONS OF NUCLEUS
Major functions of nucleus are the control of cellular activities and storage of hereditary material. Several processes are involved in the nuclear functions.
Functions of Nucleus:
- Control of all the cell activities that include metabolism, protein synthesis, growth and reproduction (cell division)
- Synthesis of RNA
- Formation of subunits of ribosomes
- Sending genetic instruction to the cytoplasm for protein synthesis through messenger RNA (mRNA)
- Control of the cell division through genes
- Storage of hereditary information (in genes) and transformation of this information from one generation of the species to the next.
More Confusing Differences in Biology:
Difference Between Metabolic Acidosis and Metabolic Alkalosis
Difference Between Pinocytosis and Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Difference Between Atrophy and Hypertrophy



Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.