Ram vs Hard Drive
Summary: Difference Between Ram and Hard Drive is that RAM (random access memory), also called main memory, consists of memory chips that can be read from and written to by the processor and other devices. While hard drive is a storage device that contains one or more inflexible, circular platters that use magnetic particles to store data, instructions, and information.
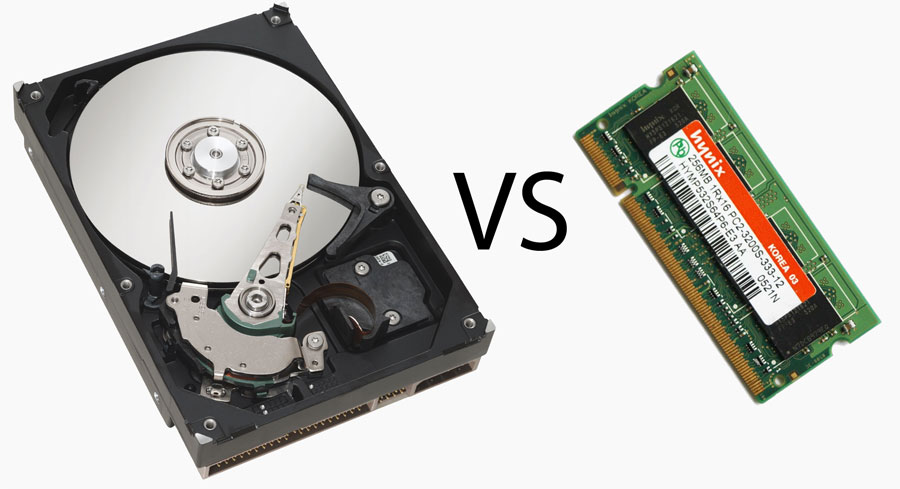
RAM
Users typically are referring to RAM when discussing computer memory. RAM (random access memory), also called main memory, consists of memory chips that can be read from and written to by the processor and other devices. When you turn on power to a computer, certain operating system files (such as the files that determine how the desktop appears) load into RAM from a storage device such as a hard disk. These files remain in RAM as long as the computer has continuous power. As additional programs and data are requested, they also load into RAM from storage.
The processor interprets and executes a program’s instructions while the program is in RAM. During this time, the contents of RAM may change. RAM can hold multiple programs simultaneously, provided the computer has enough RAM to accommodate all the programs. Most RAM is volatile, which means it loses its contents when the power is removed from the computer. For this reason, you must save any items you may need in the future. Saving is the process of copying items from RAM to a storage device such as a hard disk.
Three basic types of RAM chips exist: dynamic RAM, static RAM, and magnetoresistive RAM.
- Dynamic RAM (DRAM pronounced DEE-ram) chips must be re-energized constantly or they lose their contents. Many variations of DRAM chips exist, most of which are faster than the basic DRAM.
- Static RAM (SRAM pronounced ESS-ram) chips are faster and more reliable than any variation of DRAM chips. These chips do not have to be re-energized as often as DRAM chips, thus, the term static.
- A newer type of RAM, called magnetoresistive RAM (MRAM pronounced EM-ram), stores data using magnetic charges instead of electrical charges. Manufacturers claim that MRAM has greater storage capacity, consumes less power, and has faster access times than electronic RAM.
RAM chips usually reside on a memory module, which is a small circuit board. Memory slots on the motherboard hold memory modules.
Hard Drive
A hard disk is a storage device that contains one or more inflexible, circular platters that use magnetic particles to store data, instructions, and information. The system unit on most desktop and notebook computers contains at least one hard disk. The entire device is enclosed in an airtight, sealed case to protect it from contamination. A hard disk that is mounted inside the system unit sometimes is called a fixed disk because it is not portable. With respect to a storage medium, the term portable means you can remove the medium from one computer and carry it to another computer.
Current personal computer hard disks have storage capacities from 160 GB to 2 TB and more. Home users store documents, spreadsheets, presentations, databases, e-mail messages, Web pages, digital photos, music, videos, and software on hard disks. Businesses use hard disks to store correspondence, reports, financial records, e-mail messages, customer orders and invoices, payroll records, inventory records, presentations, contracts, marketing literature, schedules, and Web sites.
Traditionally, hard disks stored data using longitudinal recording, which aligned the magnetic particles horizontally around the surface of the disk. With perpendicular recording, by contrast, hard disks align the magnetic particles vertically, or perpendicular to the disk’s surface, making much greater storage capacities possible. Experts estimate that hard disks using perpendicular recording provide storage capacities about 10 times greater than disks that use longitudinal recording. Hard disks are read/write storage media. That is, you can read from and write on a hard disk any number of times.
Also Read:
Difference Between Internal and External Drive Bays
Difference Between Motherboard and Hard Drive
Difference Between Flash Memory and Hard Drive
Difference Between Memory and Hard Drive





Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.