Computer Buses vs Registers
Summary: Difference Between Computer Buses and Registers is that computer processes and stores data as a series of electronic bits. These bits transfer internally within the circuitry of the computer along electrical channels. While Registers are also a part of a computer processor and holding one small piece of data in Processor. A register may hold a piece of data, like a storage address and computer instruction.
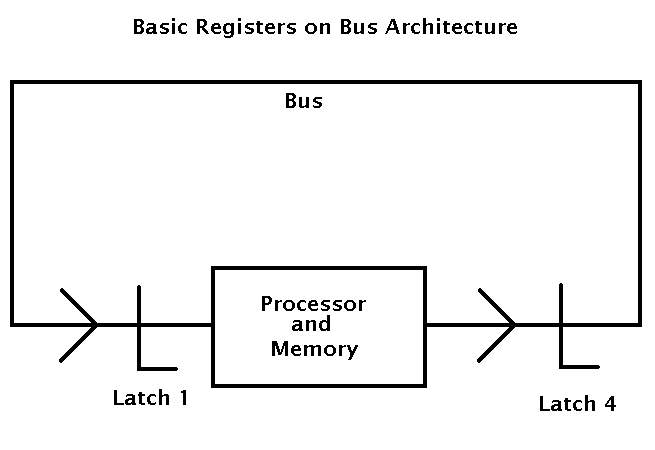
Computer Buses
A computer processes and stores data as a series of electronic bits. These bits transfer internally within the circuitry of the computer along electrical channels. Each channel, called a bus, allows the various devices both inside and attached to the system unit to communicate with each other. Just as vehicles travel on a highway to move from one destination to another, bits travel on a bus. Buses are used to transfer bits from input devices to memory, from memory to the processor, from the processor to memory, and from memory to output or storage devices. Buses consist of two parts: a data bus and an address bus. The data bus is used to transfer actual data and the address bus is used to transfer information about where the data should reside in memory.
The size of a bus, called the bus width, determines the number of bits that the computer can transmit at one time. For example, a 32-bit bus can transmit 32 bits (4 bytes) at a time. On a 64-bit bus, bits transmit from one location to another 64 bits (8 bytes) at a time. The larger the number of bits handled by the bus, the faster the computer transfers data. Most personal computers today use a 64-bit bus.
A computer has these basic types of buses: a system bus, possibly a backside bus, and an expansion bus. A system bus, also called the front side bus (FSB), is part of the motherboard and connects the processor to main memory. When computer professionals use the term bus by itself, they usually are referring to the system bus. A backside bus (BSB) connects the processor to cache. An expansion bus allows the processor to communicate with peripherals. Some peripherals outside the system unit connect to a port on an adapter card, which is inserted in an expansion slot on the motherboard. This expansion slot connects to the expansion bus, which allows the processor to communicate with the peripheral attached to the adapter card.
Registers
Registers are also a part of a computer processor and holding one small piece of data in Processor. A register may hold a piece of data, like a storage address and computer instruction. Some instructions specify registers as part of the instruction. E.g it may be specified that an instruction of two registers can be placed together on a specified register. There must be a large register enough so that it can hold instructions. For example, in a 32-Bit instruction computer, a register must be 32 bits in length. But in many computers, there are smaller registers like half registers for shorter instructions. Registers may have arbitrary or numbers names which depends on the processor designs and language rules.
Also Read:
Difference Between Cache and Register
Difference Between Memory and Register
Difference Between System Bus and Expansion Bus
Difference Between Manufacturing and Producing






Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.