Enamel vs Cementum
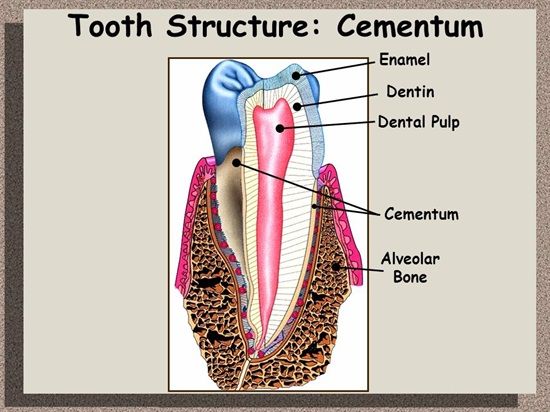
Summary: Difference Between Enamel and Cementum is that the enamel is the hardest tissue in the human body. It is the only ectodermal derivative of the tooth. Inorganic constituents account for 96% by weight and they are mainly calcium phosphate in the form of hydroxyapatite crystals. While the cementum is comparable to bone in its proportion of inorganic to organic constituents and to similarities in its structure. The cementum is thinnest at its junction with the enamel and thickest at the apex.
Enamel
The enamel is the hardest tissue in the human body. It is the only ectodermal derivative of the tooth. Inorganic constituents account for 96% by weight and they are mainly calcium phosphate in the form of hydroxyapatite crystals. These apatite crystals are arranged in the form of rods. All other hard tissues of the body, dentin, cementum and bone also have hydroxyapatite as the principal inorganic constituent. Hydroxyapatite crystals differ in size and shape; those of the enamel are hexagonal and longest.
Enamel is the only hard tissue, which does not have collagen in its organic matrix. The enamel present in the fully formed crown has no viable cells, as the cells forming it—the ameloblast degenerates, once enamel formation is over. Therefore, all the enamel is formed before eruption. This is of clinical importance as enamel lost, after tooth has erupted, due to wear and tear or due to dental caries, cannot be formed again. Enamel, lacks not only formative cells but also vessels and nerves. This makes the tooth painless and no blood oozes out when enamel is drilled while making a cavity for filling.
Cementum
The cementum is comparable to bone in its proportion of inorganic to organic constituents and to similarities in its structure. The cementum is thinnest at its junction with the enamel and thickest at the apex. The cementum gives attachment to the periodontal ligament fibers. Cementum forms throughout life, so as to keep the tooth in functional position. Cementum also forms as a repair tissue and in excessive amounts due to low grade irritants.
The cells that form the cementum; the cementoblast lines the cemental surface. Uncalcified cementum is usually seen, as the most superficial layer of cementum. The cells within the cementum, the cementocytes are enclosed in a lacuna and its process in the canaliculi, similar to that seen in bone, but in a far less complex network. Cementocytes presence is limited to certain regions.
The regions of cementum containing cells are called cellular cementum and the regions without it, are known as the acellular cementum. The acellular cementum is concerned with the function of anchorage to the teeth and the cellular cementum is concerned with adaptation, i.e. to keep the tooth in the functional position. Like dentin, cementum forms throughout life, and is also avascular and noninnervated.
Also Read:
Difference Between Enamel and Dentin
Difference Between Cementum and Dentin
Difference Between Alveolar Bone and Cementum
Difference Between Cementum and Periodontal Ligament
Difference Between Cementum and Alveolar Bone


Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.