Dentin vs Alveolar Bone
Summary: Difference Between Dentin and Alveolar Bone is that Dentin forms the bulk of the tooth. It consists of dentinal tubules, which contains the cytoplasmic process of the odontoblasts. The tubules are laid in the calcified matrix—the walls of the tubules are more calcified than the region between the tubules. While Alveolar bone is the alveolar process of the jaws that forms and supports the sockets for the teeth. They develop during the eruption of the teeth and disappear after the tooth is extracted or lost.
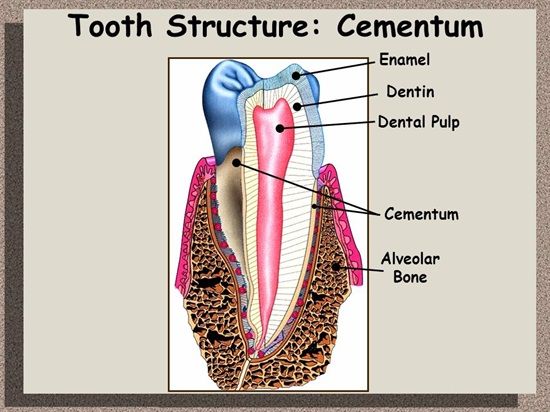
Dentin
The dentin forms the bulk of the tooth. It consists of dentinal tubules, which contains the cytoplasmic process of the odontoblasts. The tubules are laid in the calcified matrix—the walls of the tubules are more calcified than the region between the tubules. The apatite crystals in the matrix are plate like and shorter, when compared to enamel. The number of tubules near the pulp are broader and closer and they usually have a sinusoidal course, with branches, all along and at their terminus at the dentinoenamel or cementodentinal junction.
The junction between enamel and dentin is scalloped to give mechanical retention to the enamel. Dentin is avascular. Nerves are present in the inner dentin only. Therefore, when dentin is exposed, by loss of enamel and stimulated, a pain-like sensation called sensitivity is experienced. The dentin forms throughout life without any stimulation or as a reaction to an irritant. The cells that form the dentin—the odontoblast lies in the pulp, near its border with dentin. Thus, dentin protects the pulp and the pulp nourishes the dentin. Though dentin and pulp are different tissues they function as one unit.
Alveolar Bone
Alveolar bone is the alveolar process of the jaws that forms and supports the sockets for the teeth. They develop during the eruption of the teeth and disappear after the tooth is extracted or lost. The basic structure of the alveolar bone is very similar to the bone found elsewhere, except for the presence of immature bundle bone amidst the compact bone lining the sockets for the teeth.
The buccal and lingual plates of compact bone enclose the cancellous bone. The arrangement and the density of the cancellous bone varies in the upper and lower jaws and is related to the masticatory load, the tooth receives. The ability of bone, but not cementum, to form under tension and resorb under pressure makes orthodontic treatment possible.
Also Read:
Difference Between Enamel and Dentin
Difference Between Cementum and Dentin
Difference Between Alveolar Bone and Cementum
Difference Between Cementum and Periodontal Ligament
Difference Between Cementum and Alveolar Bone



Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.