Ram vs Storage
Summary: Difference Between Ram and Storage is that RAM (random access memory), also called main memory, consists of memory chips that can be read from and written to by the processor and other devices. While Storage holds data, instructions, and information for future use.
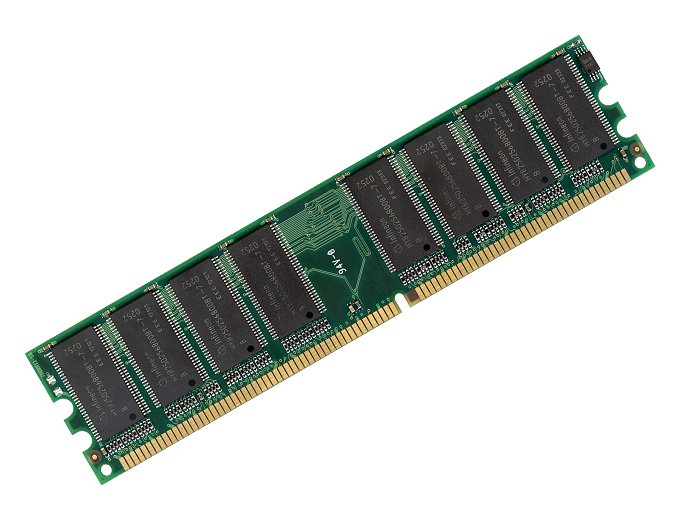

RAM
Users typically are referring to RAM when discussing computer memory. RAM (random access memory), also called main memory, consists of memory chips that can be read from and written to by the processor and other devices. When you turn on power to a computer, certain operating system files (such as the files that determine how the desktop appears) load into RAM from a storage device such as a hard disk. These files remain in RAM as long as the computer has continuous power. As additional programs and data are requested, they also load into RAM from storage.
The processor interprets and executes a program’s instructions while the program is in RAM. During this time, the contents of RAM may change. RAM can hold multiple programs simultaneously, provided the computer has enough RAM to accommodate all the programs. Most RAM is volatile, which means it loses its contents when the power is removed from the computer. For this reason, you must save any items you may need in the future. Saving is the process of copying items from RAM to a storage device such as a hard disk.
Three basic types of RAM chips exist: dynamic RAM, static RAM, and magnetoresistive RAM.
- Dynamic RAM (DRAM pronounced DEE-ram) chips must be re-energized constantly or they lose their contents. Many variations of DRAM chips exist, most of which are faster than the basic DRAM.
- Static RAM (SRAM pronounced ESS-ram) chips are faster and more reliable than any variation of DRAM chips. These chips do not have to be re-energized as often as DRAM chips, thus, the term static.
- A newer type of RAM, called magnetoresistive RAM (MRAM pronounced EM-ram), stores data using magnetic charges instead of electrical charges. Manufacturers claim that MRAM has greater storage capacity, consumes less power, and has faster access times than electronic RAM.
RAM chips usually reside on a memory module, which is a small circuit board. Memory slots on the motherboard hold memory modules.
Storage
Storage holds data, instructions, and information for future use. For example, all types of users store digital photos; appointments, schedules, and contact/address information; correspondence, such as letters, e-mail messages; tax records; and Web pages. A home user also might store budgets, bank statements, a household inventory, records of stock purchases, tax information, homework assignments, recipes, music, and videos. In addition or instead, a business user stores reports, financial records, travel records, customer orders and invoices, vendor payments, payroll records, inventory records, presentations, quotations, and contracts. Other users store diagrams, drawings, blueprints, designs, marketing literature, corporate newsletters, and product catalogs. All computers also store system and application software.
Storage requirements among users vary greatly. Home users typically have much smaller storage requirements than enterprise users. For example, a home user may need 320 GB (billion bytes) of storage, while enterprises may require 50 PB (quadrillion bytes) of storage. A storage medium (media is the plural), also called secondary storage, is the physical material on which a computer keeps data, instructions, and information. Examples of storage media are hard disks, solid state drives, memory cards, USB flash drives, ExpressCard modules, optical discs, smart cards, magnetic stripe cards, and microfilm. Cloud storage is another storage option, in which the actual storage media used is transparent to the user.
Also Read:
Difference Between Memory and Storage
Difference Between Flash Memory and Cache Memory
Difference Between Memory and Flash Storage
Difference Between Flash Memory and Ram





Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.