Respiratory Acidosis vs Respiratory Alkalosis
Summary: Difference Between Respiratory Acidosis and Respiratory Alkalosis is that Respiratory acidosis is the acidosis that is caused by alveolar hypoventilation. While Respiratory alkalosis is the alkalosis that is caused by alveolar hyperventilation.
Respiratory Acidosis
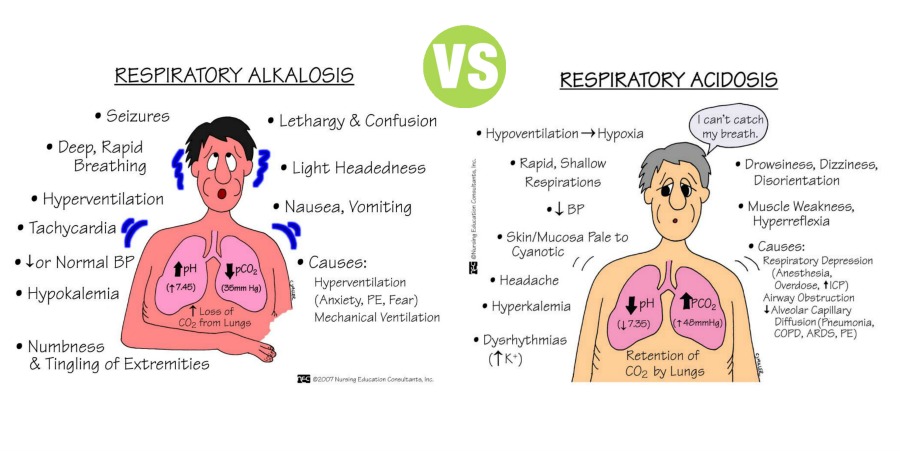
Respiratory acidosis is the acidosis that is caused by alveolar hypoventilation. During hypoventilation the lungs fail to expel CO2 , which is produced in the tissues. CO2 is the major end product of oxidation of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. CO2 accumulates in blood where it reacts with water to form carbonic acid, which is called respiratory acid. Carbonic acid dissociates into H+ and HCO3 – . The increased H+ concentration in blood leads to decrease in pH and acidosis.
Normal partial pressure of CO2 in arterial blood is about 40 mm Hg. When it increases above 60 mm Hg acidosis occurs.
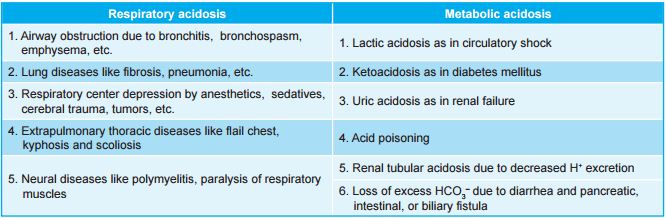
Causes of Excess CO2 in the Body
Hypoventilation (decreased ventilation) is the primary cause for excess CO2 in the body. Some of the conditions when increase in pCO2 and respiratory acidosis occur due to hypoventilation are listed in image below.
Causes of Decrease in CO2 in the Body
Hyperventilation is primary cause for loss of excess CO2 from the body because during hyperventilation, lot of CO2 is expired through respiratory tract leading to decreased pCO2 . Some of the conditions when decreased pCO2 and respiratory alkalosis occur due to hyperventilation are given in image below.

Respiratory Alkalosis
Respiratory alkalosis is the alkalosis that is caused by alveolar hyperventilation. Hyperventilation causes excess loss of CO2 from the body. Loss of CO2 leads to decreased formation of carbonic acid and decreased release of H+. Decreased H+ concentration increases the pH leading to respiratory alkalosis. When the partial pressure of CO2 in arterial blood decreases below 20 mm Hg, alkalosis occurs.
Causes of Decrease in CO2 in the Body
Hyperventilation is primary cause for loss of excess CO2 from the body because during hyperventilation, lot of CO2 is expired through respiratory tract leading to decreased pCO2 . Some of the conditions when decreased pCO2 and respiratory alkalosis occur due to hyperventilation are given in image below.

More Confusing Differences in Biology:
Difference Between Metabolic Acidosis and Metabolic Alkalosis



Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.