Difference Between Internet Intranet and Extranet
Summary: Difference Between Internet Intranet and Extranet is that Internet, also called the Net, is a worldwide collection of networks that links millions of businesses, government agencies, educational institutions, and individuals. An intranet (intra means within) is an internal network that uses Internet technologies. Intranets generally make company information accessible to employees and facilitate working in groups. An extranet is the portion of a company’s network that allows customers or suppliers of a company to access parts of an enterprise’s intranet. An extranet provides a secure, physical connection to the company’s network.
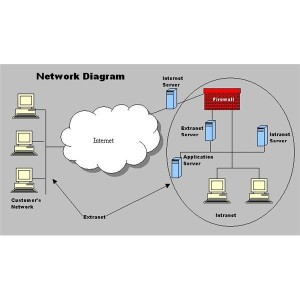
Internet
One of the major reasons business, home, and other users purchase computers is for Internet access. The Internet, also called the Net, is a worldwide collection of networks that links millions of businesses, government agencies, educational institutions, and individuals. The Internet is a widely used research tool, providing society with access to global information and instant communications.
Today, more than one billion home and business users around the world access a variety of services on the Internet. The World Wide Web, or simply the Web, and e-mail are two of the more widely used Internet services. Other services include chat rooms, instant messaging, and VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol).
The Internet has its roots in a networking project started by an agency of the U.S. Department of Defense. The goal was to build a network that (1) allowed scientists at different locations to share information and work together on military and scientific projects and (2) could function even if part of the network were disabled or destroyed by a disaster such as a nuclear attack. That network, called ARPANET, became functional in September 1969, linking scientific and academic researchers across the United States.
The original ARPANET consisted of four main computers, one each located at the University of California at Los Angeles, the University of California at Santa Barbara, the Stanford Research Institute, and the University of Utah. Each of these computers served as a host on the network. A host or server is any computer that provides services and connections to other computers on a network. By 1984, ARPANET had more than 1,000 individual computers linked as hosts. Today, more than 550 million hosts connect to this network, which is known now as the Internet.
The Internet consists of many local, regional, national, and international networks. Both public and private organizations own networks on the Internet. These networks, along with telephone companies, cable and satellite companies, and the government, all contribute toward the internal structure of the Internet.
Each organization on the Internet is responsible only for maintaining its own network. No single person, company, institution, or government agency controls or owns the Internet. The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), however, oversees research and sets standards and guidelines for many areas of the Internet. More than 350 organizations from around the world are members of the W3C.
Intranet
Recognizing the efficiency and power of the Internet, many organizations apply Internet and Web technologies to their internal networks. An intranet (intra means within) is an internal network that uses Internet technologies. Intranets generally make company information accessible to employees and facilitate working in groups. Simple intranet applications include electronic publishing of organizational materials such as telephone directories, event calendars, procedure manuals, employee benefits information, and job postings. Additionally, an intranet typically includes a connection to the Internet. More sophisticated uses of intranets include groupware applications such as project management, chat rooms, newsgroups, group scheduling, and video conferencing.
An intranet essentially is a small version of the Internet that exists within an organization. Users update information on the intranet by creating and posting a Web page, using a method similar to that used on the Internet. Sometimes a company uses an extranet, which allows customers or suppliers to access part of its intranet. Package shipping companies, for example, allow customers to access their intranet to print air bills, schedule pickups, and even track shipped packages as the packages travel to their destinations.
Extranet
An extranet is the portion of a company’s network that allows customers or suppliers of a company to access parts of an enterprise’s intranet. An extranet provides a secure, physical connection to the company’s network. Customers may use the extranet to place and monitor orders electronically or to make payments. Suppliers may check inventory levels of the parts they supply to the company and receive orders and payments from the company. Extranet improve efficiency by replacing the postal service, faxes, or telephone calls as the communications medium of choice.
Also Read:
Difference Between Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Computer
Difference Between Servers and Mainframes
Difference Between Personal Computers and Game Consoles






Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.