SATA vs SAS
Summary: Difference Between SATA and SAS is that SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) uses serial signals to transfer data, instructions, and information. While SAS (serial-attached SCSI) is a newer type of SCSI that uses serial signals to transfer data, instructions, and information.
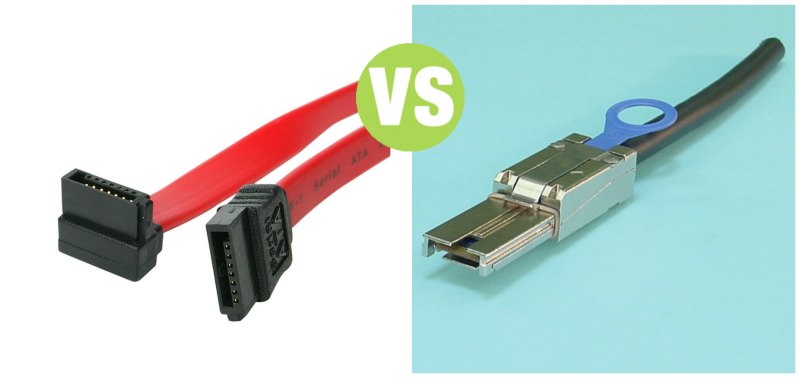
SATA
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) uses serial signals to transfer data, instructions, and information. The primary advantage of SATA interfaces is their cables are thinner, longer, more flexible, and less susceptible to interference than cables used by hard disks that use parallel signals. SATA interfaces also support connections to optical disc drives. External disks use the eSATA (external SATA) interface, which is much faster than USB and FireWire.
SAS
SAS (serial-attached SCSI) is a newer type of SCSI that uses serial signals to transfer data, instructions, and information. Advantages of SAS over parallel SCSI include thinner, longer cables; reduced interference; less expensive; support for many more connected devices at once; and faster speeds. In addition to hard disks, SAS interfaces support connections to optical disc drives, printers, scanners, digital cameras, and other devices. Experts predict that SAS eventually will replace parallel SCSI.
Also Read:
Difference Between SATA and EIDE
Difference Between SATA and SCSI






Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.