Difference Between Hard Disk and Solid State Drives
Summary: Difference Between Hard Disk and Solid State Drives is that a hard disk is a storage device that contains one or more inflexible, circular platters that use magnetic particles to store data, instructions, and information. A solid state drive (SSD) is a storage device that typically uses flash memory to store data, instructions, and information.
Hard Disk
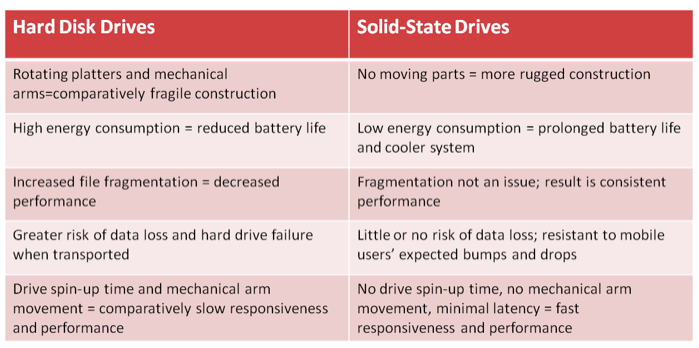
A hard disk is a storage device that contains one or more inflexible, circular platters that use magnetic particles to store data, instructions, and information. The system unit on most desktop and notebook computers contains at least one hard disk. The entire device is enclosed in an airtight, sealed case to protect it from contamination. A hard disk that is mounted inside the system unit sometimes is called a fixed disk because it is not portable. With respect to a storage medium, the term portable means you can remove the medium from one computer and carry it to another computer.
Current personal computer hard disks have storage capacities from 160 GB to 2 TB and more. Home users store documents, spreadsheets, presentations, databases, e-mail messages, Web pages, digital photos, music, videos, and software on hard disks. Businesses use hard disks to store correspondence, reports, financial records, e-mail messages, customer orders and invoices, payroll records, inventory records, presentations, contracts, marketing literature, schedules, and Web sites.
Traditionally, hard disks stored data using longitudinal recording, which aligned the magnetic particles horizontally around the surface of the disk. With perpendicular recording, by contrast, hard disks align the magnetic particles vertically, or perpendicular to the disk’s surface, making much greater storage capacities possible. Experts estimate that hard disks using perpendicular recording provide storage capacities about 10 times greater than disks that use longitudinal recording. Hard disks are read/write storage media. That is, you can read from and write on a hard disk any number of times.
Solid State Drives
A solid state drive (SSD) is a storage device that typically uses flash memory to store data, instructions, and information. With available sizes of 3.5 inches, 2.5 inches, and 1.8 inches, SSDs are used in all types of computers including servers, desktop computers, and mobile computers and devices such as portable media players and digital video cameras.
Storage capacities of current SSDs range from 16 GB to 256 GB and more. SSDs have several advantages over magnetic hard disks.
- Access times of SSDs are about 0.1 ms, which is more than 80 times faster than a hard disk.
- Transfer rates of SSDs are faster than comparable hard disks.
- SSDs generate less heat and consume less power than hard disks.
- Manufacturers claim that SSDs will last more than 50 years, which is much greater than the 3 to 5 year hard disk stated lifespan.
The disadvantages of SSDs are they currently have a higher failure rate than hard disks, and their cost is much higher per gigabyte. As the price of SSDs drops, experts estimate that increasingly more users will purchase computers and devices that use this media.
Also Read:
Difference Between Motherboard and CPU
Difference Between System Unit and Peripheral
Difference Between Buffer and Cache
Difference Between Mission and Vision Statement





Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.